The Risk Factors of Cardiac Arrest.
1 min read
(Continued from last week.)

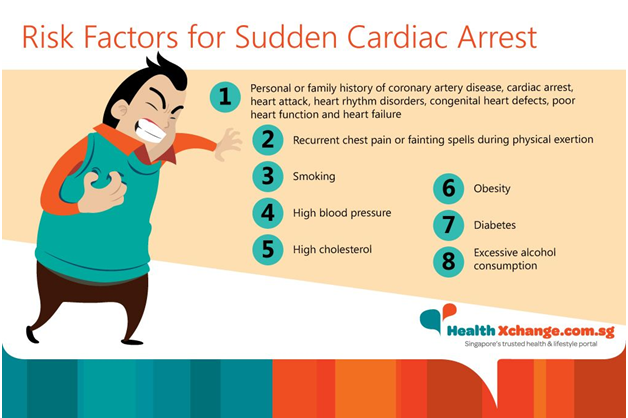
Risk factors: Because sudden cardiac arrest is so often linked with coronary artery disease, the same factors that put you at risk of coronary artery disease can also put you at risk of sudden cardiac arrest. These include:
A family history of coronary artery disease. Smoking
High blood pressure
High blood cholesterol
Obesity
Diabetes
An inactive lifestyle.
Other factors that might increase your risk of sudden cardiac arrest include:
A previous episode of cardiac arrest or a family history of cardiac arrest
A previous heart attack. A personal or family history of other forms of heart disease, such as heart rhythm disorders, congenital heart defects, heart failure and cardiomyopathy.
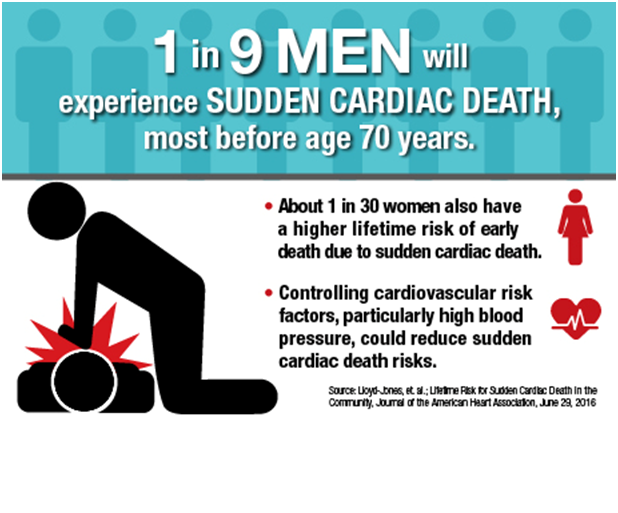
Growing older — the risk of sudden cardiac arrest increases with age
Being male
Using illegal drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines
Nutritional imbalance, such as low potassium or magnesium levels
Obstructive sleep apnea
Chronic kidney disease
Complications: When sudden cardiac arrest occurs, reduced blood flow to your brain causes unconsciousness. If your heart rhythm doesn’t rapidly return to normal, brain damage occurs and death results. Survivors of cardiac arrest might show signs of brain damage.
More Information: Sudden cardiac arrest care at Mayo Clinic
Sudden death in young people: Heart problems often blamed.
Prevention: Reduce your risk of sudden cardiac arrest by getting regular checkups, being screened for heart disease and living a heart-healthy lifestyle.




